Pneumonia: Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention
Pneumonia is a transmittable infection with mild to severe symptoms. The severity of your pneumonia relies on the specific bacteria causing it, your overall health, and your age. Pneumonia can affect anyone.
Young children, seniors, and those with pre-existing immune-system-compromising medical disorders are the groups of people who have a higher risk of contracting pneumonia. The risk of pneumonia-related complications is likewise higher in these similar groups of individuals. Hence, in
2019, pneumonia was responsible for 14% of all deaths among children under five.
So let's take a look at the symptoms you should be looking out for, the treatments available and ways to prevent you or your loved ones from contracting this illness.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a lung infection caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The infection causes the alveoli, or lung air sacs, to become inflamed. Breathing becomes challenging because the alveoli are filled with fluid or pus.
Both bacterial and viral pneumonia are easily transmissible. This means they can transmit from person to person via inhalation of airborne droplets from a sneeze or cough. You can also contract various types of pneumonia by touching surfaces or objects infected with pneumonia-causing bacteria or viruses.
On the other hand, pneumonia caused by fungi can be transmitted through the air. However, it cannot spread from one individual to another.
Pneumonia is further divided into categories based on how or where it was acquired:
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP): This particular bacterial pneumonia is contracted while being hospitalised. As the bacteria involved might be more antibiotic-resistant than other types, it could be more dangerous.
- Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): This type of pneumonia is contracted outside of a medical or institutional setting.
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP): VAP, or ventilator-associated pneumonia, is pneumonia that affects individuals who are using a ventilator.
- Aspiration pneumonia: Aspiration pneumonia is caused by inhaling bacteria into your lungs through food, drink, or saliva. It's more likely to happen if you have a swallowing problem or are very drowsy from medication, alcohol, or other drugs.
What are the symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can range from minor to fatal. They may include the following:
- Coughing that may produce phlegm (mucus)
- Fever
- Sweating or chills
- Shortness of breath that happens while doing everyday activities or even while resting
- Chest pain that's worse when you breathe or cough
- Feelings of tiredness or fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headaches
Depending on your age and general health, other symptoms may also occur:
- Infants may seem asymptomatic but occasionally vomit, fatigue, or have problems drinking or eating.
- Children under the age of five may experience rapid breathing or wheezing.
- Older adults may experience milder effects. However, they may become confused or have a lower body temperature than usual.
What are the basic Pneumonia Diagnosis tests
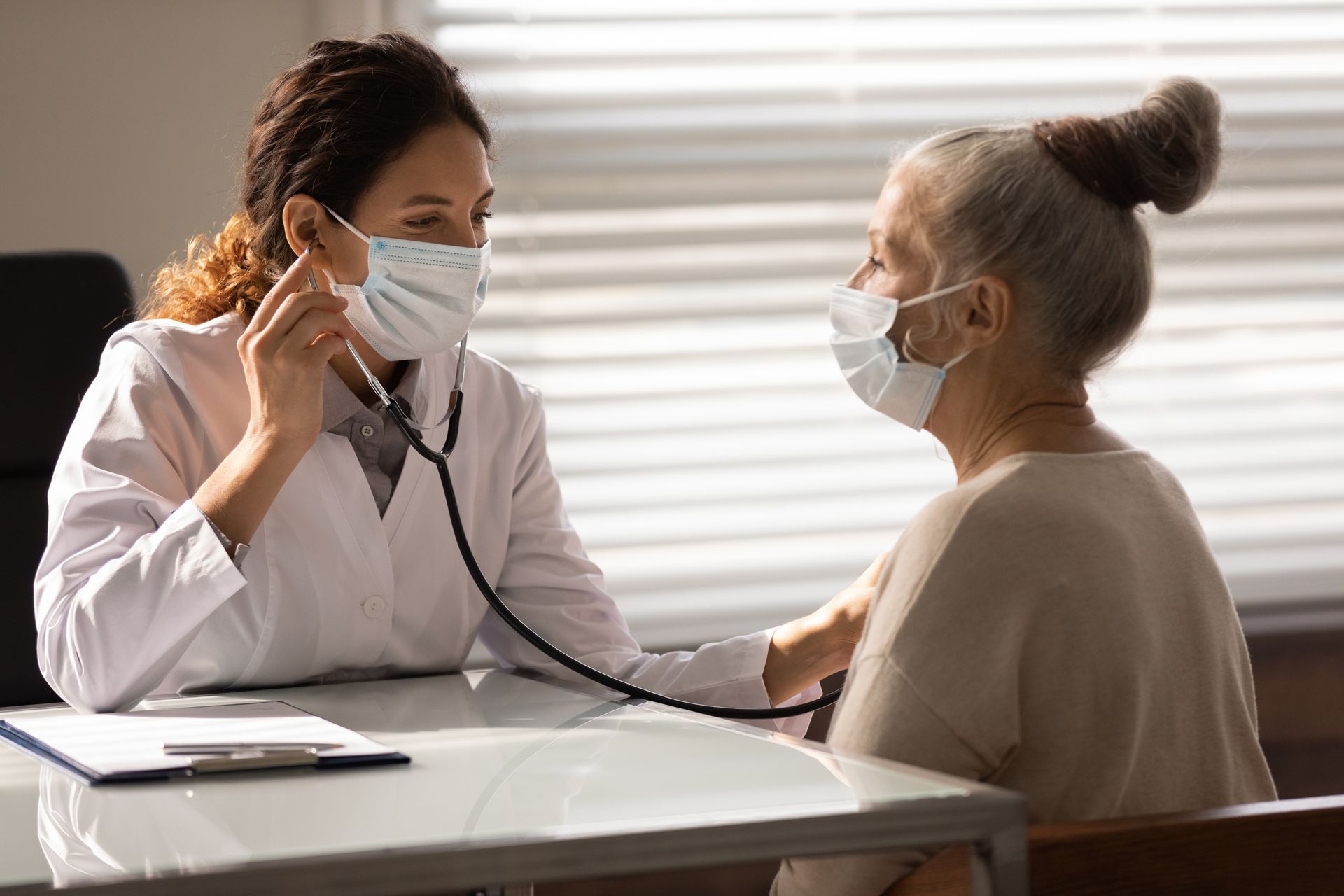
Your medical history will be gathered in the beginning by your doctor. They'll inquire about your general health and the timing of the occurrence of your symptoms.
The next step is a physical examination. This will involve using a stethoscope to listen to your lungs for unusual noises, such as crackling.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of the following tests, depending on the severity of your symptoms and your risk of complications:
Blood Tests
A blood sample is used in this test to confirm an infection. Additionally, culturing can aid in determining what might be the root of your illness.
Chest X-ray
An X-ray helps your specialist in checking for symptoms of chest inflammation. Your doctor can understand more about the location and severity of any inflammation from the X-ray if it is present.
Pulse Oximetry
The amount of oxygen in your blood is measured with a pulse oximetry. A sensor that is fitted on one of your fingertips can tell you if your lungs are delivering enough oxygen to your bloodstream.
Sputum Test
To help identify the infection's origin, your doctor may take a sample of the fluid from your lungs (sputum) after a strong cough.
CT Scan
Your doctor could prescribe a chest CT scan to get a more precise image of your lungs if your pneumonia isn't improving as promptly as expected.
Pleural Fluid Culture
A fluid sample from the pleural area is drawn using a needle inserted between your ribs to identify the type of infection.
Treatment for Pneumonia
Antibiotics should be used to treat pneumonia. Amoxicillin dispersible pills are the preferred antibiotic for the first treatment. Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic with a broad spectrum of effects used to treat bacterial infections.
Most pneumonia infections require oral antibiotics, which are frequently provided at a health centre. Trained community health workers can also identify these cases and treat them locally with affordable oral antibiotics. Only the most severe pneumonia cases should be hospitalised.
Prevention
Pneumococcal illness, the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia, can be prevented using two different vaccines. The immunisations offer defence against numerous pneumococcal illnesses.
While they may not protect older adults against pneumonia, they can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia and other S. pneumoniae infections, such as blood and brain infections. There are two vaccines for pneumonitis, which are as follows:
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, often known as Prevnar or PCV13, is a pneumococcal vaccine. Doctors recommend PCV13 for the following groups:
- Children under two years old, as PCV13 is a typical part of an infant's routine immunisations
- Those ages two years or above who have certain underlying medical conditions
Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine
Doctors may also refer to the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination as Pneumovax or PPSV23. Doctors recommend PPSV23 for the following groups:
- Individuals ages 2–64 years who have certain underlying medical conditions, such as:
- Diabetes
- Chronic heart, lung, or kidney disease
- Lack of a spleen due to surgical removal
- Adults ages 19–64 years who smoke cigarettes
- All adults ages 65 years or above
In addition to vaccinations, doctors recommend the following precautions to help prevent pneumonia:
- Washing your hands regularly
- Covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Avoid smoking
- Eating a balanced, nutritious diet
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid people who have pneumonia, or be extra vigilant about hygiene when around people who are ill
Generally, pneumonia gets better within a few weeks. If your symptoms worsen, consult a doctor immediately since you might need to be hospitalised to prevent or treat more severe complications.
Looking for lung screening in Singapore? Get specialist care at Respiratory Medical Associates
Respiratory Medical Associates is an established specialist group that is recognised as one of Singapore’s leading experts in the diagnosis and treatment of lung, sleep, and allergy disorders. These can range from persistent coughs, spots on the chest X-ray to lung infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
In addition, we also treat chronic disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (a lung disease caused by smoking), lung fibrosis, obstructive sleep apnoea, as well as food and drug allergy. Enquire now at https://www.respmed-associates.sg/